Everybody working on an excavation on site or in post-excavation performs one or more roles. Each role represents the knowledge and skills that an individual is expected to have in order to perform the role and the responsibilities that will be assigned to them while performing the role. Around the internet, lots has been posted about roles and their associated archaeological knowledge, skills and responsibilities.
Overview of the roles
The following table lists the roles, the contribution people performing those roles make to an excavation and the equipment and IT applications they are expected to use.
Roles for archaeologists
| Role | Responsibility for excavation | Equipment and IT applications used by this role |
| Project leader | Has complete control of a site and work on the site | Everything on and off site |
| Surveyor | Geo-positions and record grids for site, geophysics and excavation areas | Global Positioning System (GPS), Total Station, using shared filestore and QGIS as an editor and a browser |
| Geophysics specialist | Collects and interprets geophysics data | Earth resistance meter, Gradiometer, Snuffler, shared filestore and QGIS as an editor and a browser |
| Site photographer | Taking pictures of the site for reports and publicity | Camera equipment to take vertical pictures on site and find images. Software to combine camera pictures, |
| Excavation area leader | Has control of an excavation area and records data about that area | Excavation tools (trowels, mattocks, markers, etc), a Dumpy level, context recording sheets, kit for drawing plans and sections, using camera to take pictures of contexts and sections, drawing stratigraphic matrices using DRAW IO |
| Digger | Digs trenches and records data | Excavation tools (trowels, mattocks, markers, etc), context recording sheets, gradually using the tools used by the Excavation area leader |
| Stratigraphic analysis recorder | Records contexts, matrices using DrawIO plans using QGIS as a browser | Recording in contexts, matrices, plans and sections in the filestore and database, drawing matrices |
| QGIS specialist | Records plans of contexts, small finds and sections | Inputs plan records using QGIS as a plan editor. Producing QGIS figures for reports |
| Finds specialist | Identifies and advises on finds and findgroups for one or more material types. | a third party offering advice and guidance |
| Finds recorder | Shadows a finds specialist, defines finds spreadsheets and tables, records finds and find groups, write finds report | Creates finds spreadsheets. Works with IT team to create specialist finds tables and queries on tables. Adds finds data to spreadsheets and tables. Uses MS office to write finds reports |
| Site interpreter | Responsible for the interpretation of a site and writing up reports | Anchurus II interpretation combining stratigraphic analysis and finds from this site with similar evidence from adjacent sites |
| Site Data specialist | Managing the site data, inputting find specialist table definitions, writing SQL queries | Anchurus II |
Information Technology roles
| Role | Responsibility | Tools they use |
| System administrator | Has complete control of a system | Anchurus II |
| System developer | Writes and tests Anchurus code | Coding and testing systems |
| System tester | Test Anchurus II | Test systems |
| System support | Works with Site Data specialists |
Shared drive access permissions
The Site Shared Drive is normally owned by the Project leader who then gives access to folders in the shared drive to people working in the roles summarised above.
Anchurus II uses a Google Drive because the Berkshire Archaeological Society, who initiated work on Anchurus, was a Not for Profit Organisation and hence was granted free use of a Google Drive.
Using Google Drive, each site has a shared drive. The project leader can download and access the Anchurus II deliverable which creates the file store structure shown below and can then select any folder or file in the structure and grant a person working on the project access to it. The access permissions are:
- Viewer: Can only view the file or folder
- Commenter: Can view and add comments to the file or files in a folder
- Editor: Can view, comment, and make edits to the content of the file or files in a folder
- Owner: Has all editor permissions and can also delete the files or folder in the shared drive
The project leader has Owner permissions and can grant these permissions to others.
The shared filestore has been designed so that the management information is in folders SC01, SC02 and SC04 and hence can be tightly controlled, and yet they can give everybody working on the project Viewer access to folder SC03 Site Archaeology and everything it contains.
The table below shows the recommended permissions assigned to the roles outlined above.
The Site shared filestore as defined in the Anchurus II deliverable is described in more detail on the following page: A Shared Filestore.
The Anchurus II database
The database management system used to support Anchurus is MariaDB. MariaDB is an open source system and available as free software.
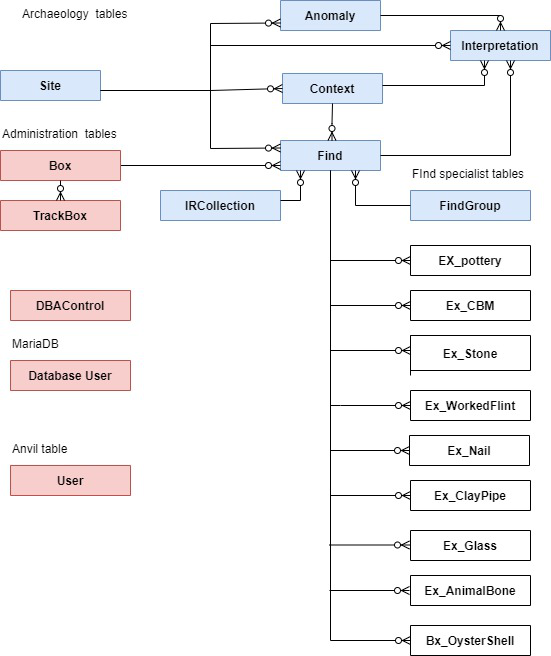
The figure below shows the tables held in the database supported by Anchurus II release 2;
The Tables shown in blue are the tables used to record the archaeology. Those shown in red are tables used to administer the finds boxes and the system. The boxes shown in white are the find specialist tables.
These tables have been designed so an Anchurus II system can record data from many different archaeological fieldwork sites.
Anchurus II database access permissions
The database management system will allow us to use the user roles defined above to control access to individual tables or even columns of tables. However, this is over complicated for what we need at this point in time so Anchurus II supports a simpler system where users and their roles are registered at site level.
The actions a user can perform on the database tables are:
- Read: all the columns in a table
- Select: a row in the table
- Insert: create a new row in a table
- Update: update a row in a table
- Write queries: these are read only queries written in SQL
For more details on these basic operations go the MariaDB website: read the documentation and watch the tutorials.
The database user roles are:
- Viewer: users assigned this role can read the site data from all the archaeological tables in the database
- Editor: users assigned this role can add new rows to the archaeological tables for a site and edit existing rows in these tables
- Manager: users assigned this role can bulk load data into the archaeological tables, delete rows from the archaeological tables and have full access to the administration tables.
- Administrator: who has complete control of and access to all the tables in the database.
The table below shows the recommended privileges that site managers should assign people performing roles on their site.
| Role | Privileges | Recommended Anchurus II roles |
| Project leader | Site archaeology and admin tables: read, select, insert, update and writing queries | Manager |
| Surveyor | Site archaeology tables: read | Viewer |
| Geophysics specialist | Site archaeology tables read, and generate queries, Anomaly table: select, insert, update | Editor |
| Trench leader | Site archaeological tables: read, generate queries Context table: select, insert, update | Editor |
| Digger | Site archaeological tables: read | Viewer |
| QGIS specialist | Site archaeological tables: read | Viewer |
| Finds specialist | Site archaeological tables and specialist finds tables: read, queries | Viewer |
| Finds recorder | Site archaeological tables: read, queries Find and Find specialist tables: select, insert, update | Editor |
| Site interpreter | Site archaeological tables: select, insert, update, queries | Editor |
| Site Data specialist | Site archaeological tables: select, insert, update queries | Manager |
| System administrator | All tables select, insert, update, queries | Administrator |
| System developer | All in test systems only | Manager |
| System tester | All in test systems only | Manager |
| Support | Given permission to access site archaeological tables by the project leader or Site data specialist | Manager |
Author: Andrew Hutt January 2026